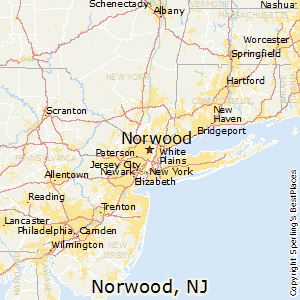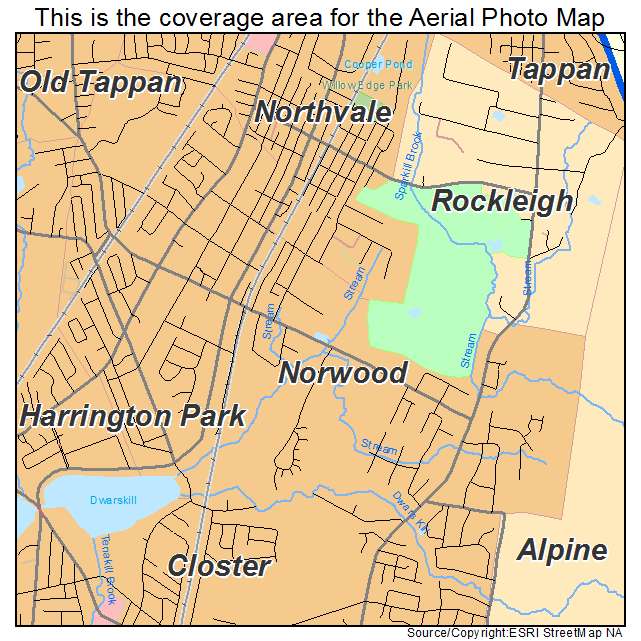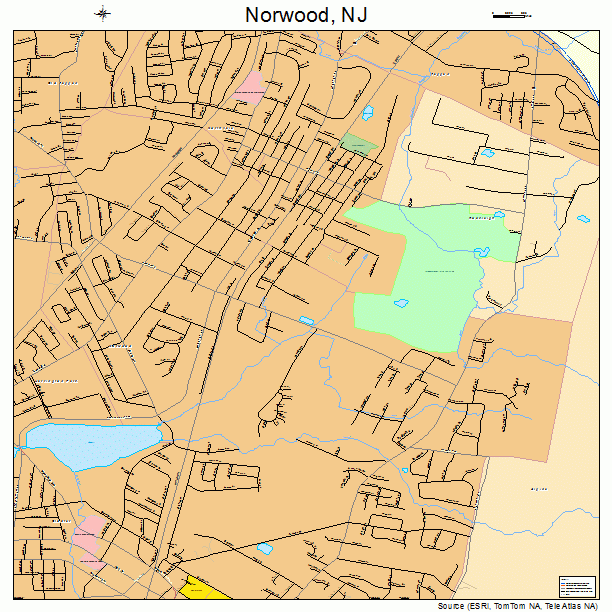
Norwood, New Jersey (NJ 07648) profile: population, maps, real estate, averages, homes, statistics, relocation, travel, jobs, hospitals, schools, crime, moving, houses, news, sex offenders

NORWOOD NJ Community Information, Demographics, Amenities and School Information - New Jersey Multiple Listing Service

NORWOOD NJ Community Information, Demographics, Amenities and School Information - New Jersey Multiple Listing Service